Why Are People Left-Handed? Genetics, Brain, and the 10% That Stand Out

About 10% of the world’s population is left-handed, making them a small but fascinating minority.
While most of us instinctively use our right hand for everyday tasks, a smaller portion of the population naturally prefers the left. But why? What makes some people left-handed, and is there a reason this trait persists across generations?
Let's unravel the mystery of the 10%.
The Role of Genetics
Hand preference isn’t completely random.
Genetics play a little role in determining handedness. Left-handedness often runs in families, and studies of twins suggest that identical twins are more likely to share the same hand preference than fraternal twins.
However, there isn’t a single “left-handed gene.” Instead, multiple genes influence handedness, interacting in ways that aren’t fully understood.
Genetic factors create a tendency toward one hand, but environment and development during pregnancy can also tip the balance.
This explains why two children in the same family may have different hand preferences, even when genetics favors one side. The brain’s wiring and early development help decide which hand becomes dominant.
The Brain Influence
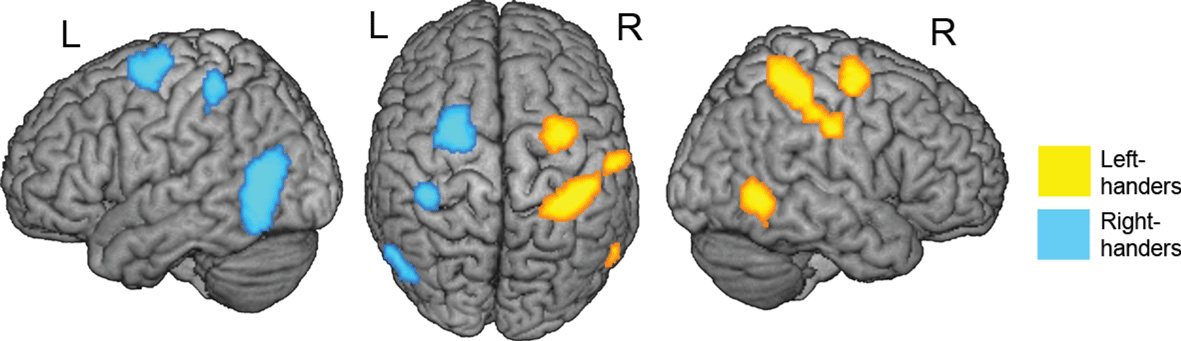
Handedness is closely tied to how our brains are organized.
The human brain has two halves, called hemispheres.
Social Insight
Navigate the Rhythms of African Communities
Bold Conversations. Real Impact. True Narratives.
For most people, the left hemisphere controls language and fine motor skills, while the right handles spatial and creative tasks.
Right-handed people usually have left-brain dominance, but left-handed people are more varied.
Many still rely on the left hemisphere, while some use the right more, or have a more balanced brain.
So left-handed brains aren’t just a mirror image, they’re wired a little differently, which can sometimes give advantages in tasks that use both sides of the brain.
This unique brain wiring might explain why left-handed people sometimes excel in creative thinking, sports, and certain types of problem-solving. However, the scientific evidence is mixed, and being left-handed doesn’t automatically make someone smarter or more creative.
Evolutionary Theories
Left-handedness is relatively rare. If it were disadvantageous, left-handedness might have disappeared over time, but it hasn’t.
One theory is that left-handedness provides an advantage in certain situations, such as combat or competitive sports. Being unpredictable can give left-handers an edge when facing predominantly right-handed opponents.
Another idea is that left-handedness exists due to “frequency-dependent selection.” In simple terms, because most people are right-handed, being left-handed provides a niche advantage. But since too many left-handers could reduce that advantage, the trait remains relatively uncommon.
Evolution alone doesn’t give us all the answers, but it suggests that left-handedness has survived because it can occasionally benefit individuals in ways that improve their chances of survival or success.
Environmental and Developmental Factors

Left-Handedness Is Influenced by Early Life Factors
While genes and brain structure play major roles, environmental and developmental factors also influence handedness.
During pregnancy, factors such as stress, hormone levels, or birth complications can affect which hand a child prefers.
Culture and upbringing historically shaped handedness as well. In many societies, children were forced to use their right hand, sometimes causing a natural left-hander to switch. Today, left-handedness is widely accepted, and children are encouraged to use their dominant hand freely.
Social Insight
Navigate the Rhythms of African Communities
Bold Conversations. Real Impact. True Narratives.
This combination of genetics, brain development, and environmental influence makes handedness a complex and fascinating human trait.
The Myths Surrounding Left-Handedness

Throughout history, left-handedness has carried both stigma and admiration.
In the past, being left-handed was often seen as a bad sign. In some cultures, the left hand was linked to bad luck or even evil. The word “sinister” actually comes from the Latin word for “left.”
In parts of Europe, left-handedness was once connected to witchcraft. Many children were even forced to use their right hand in school, as if being left-handed was something wrong that needed to be fixed.
Today, we know that isn’t true. Left-handedness is a normal part of human variation. It is not a flaw or a problem. In fact, forcing children to switch hands can cause stress and learning difficulties.
There is also a popular belief that left-handers are more creative. Famous left-handed artists and leaders often fuel this idea. Some research suggests there may be small differences in how left-handed brains are wired, which could influence certain types of thinking.
But creativity depends on many factors — personality, experience, and environment. Being left-handed does not automatically make someone more creative, just as being right-handed does not limit creativity.
In the end, left-handedness is neither unlucky nor magical. It is simply one of the many natural differences between people.
Left-Handedness in Daily Life
Left-handed people often navigate a world designed for right-handers.
Scissors, desks, kitchen tools, and musical instruments are typically built for the majority. While this can be challenging, left-handers often develop unique strategies and skills to adapt.
Left-handedness emerges from a mix of genetics, brain structure, evolutionary pressures, and environmental factors. While it’s less common than right-handedness, it has persisted throughout history, giving rise to unique abilities and perspectives.
You may also like...
Super Eagles Coach in Turmoil: Eric Chelle's Sky-High Demands Rock NFF

Super Eagles coach Eric Chelle is embroiled in a salary dispute with the Nigeria Football Federation, demanding a monthl...
Arsenal's Title Dream in Jeopardy After Stunning Wolves Comeback

Arsenal's Premier League title hopes took a major hit after they blew a two-goal lead to draw 2-2 with Wolves, facing re...
Cillian Murphy's Tommy Shelby Returns in Epic 'Peaky Blinders' Movie Trailer

"Peaky Blinders: The Immortal Man" sees Cillian Murphy's Tommy Shelby return from exile in 1940 Birmingham, confronting ...
Shocking Revelations: Joyous Celebration Directors Locked in Bitter Financial Dispute!

A significant financial dispute has emerged within the renowned South African gospel group, Joyous Celebration. Co-found...
New Skies: Benin's Amazone Airlines Forges Key Middle East Travel Link

Benin has launched its new national flag carrier, Amazone Airlines, on February 13, 2026, in a strategic partnership wit...
Paradise Restored: Remote St Helena Reopens with Airlink Flights

After a week-long grounding due to critical firefighting equipment faults, St Helena Airport has successfully reopened w...
Millions Stranded: Healthcare System Faces Catastrophic Surgery Cancellations

A critical global shortage of bone cement has forced the cancellation of tens of thousands of joint replacement surgerie...
Horror Delay: Endometriosis Patient's Long Wait Reveals Terminal Cancer

Tamara Mulley's journey began with suspected endometriosis but led to a stage 4 cholangiocarcinoma diagnosis at just 27,...