8 Things That Only Happen in Your Sleep And Why They Matter

Sleep is often mistaken as a passive state, a quiet pause when the body and brain simply power down. But modern science shows that sleep is one of the most active and mysterious processes of human life. Beneath closed eyelids, your brain fires with electrical storms, your body repairs microscopic injuries, and your mind wanders through landscapes of memory and imagination. In fact, some things that are crucial for survival happen only while you sleep.
The Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) considers sleep a pillar of health, alongside diet and exercise. Yet, nearly one in three adults worldwide report insufficient sleep, a fact that has serious consequences for memory, immunity, emotional balance, and even life expectancy.
Here are eight remarkable processes that occur exclusively during sleep, and why they matter more than you think.
1. Memory Consolidation
When you’re asleep, your brain doesn’t stop working—it reorganizes. During deep non-REM sleep and especially REM sleep, the brain replays and sorts through the information you took in during the day. This process, called memory consolidation, moves data from short-term storage (the hippocampus) into long-term memory banks in the neocortex.
A 2017 study in Current Biology found that sleep strengthens the neural connections that underlie learning. In fact, students who slept after studying remembered 40% more material than those who stayed awake.
Without proper sleep, even hours of study or practice won’t “stick.” This is why pulling all-nighters before an exam often backfires—your brain needs those hours of sleep to seal the information in place.
2. Physical Repair and Growth
Ever heard of “beauty sleep”? Science backs it up. During slow-wave sleep, your body releases growth hormone (GH), which is essential for tissue repair, muscle recovery, and bone growth. GH secretion peaks during the first deep sleep cycles of the night and is nearly absent during wakefulness.
Athletes, for example, see measurable differences in performance and recovery when they get sufficient sleep. The American Academy of Sleep Medicine notes that inadequate sleep impairs reaction time, coordination, and recovery. Conversely, well-rested athletes build muscle faster and sustain fewer injuries.
Cuts heal faster, sore muscles repair more efficiently, and your skin rejuvenates—all because your body dedicates night time hours to cellular maintenance.

Photo Credit: Pinterest
3. Brain Detox: The Glymphatic System
One of the most fascinating discoveries in neuroscience came in 2012: the glymphatic system, the brain’s waste-clearance system, becomes highly active during sleep. This system flushes out toxic proteins like beta-amyloid, which are linked to Alzheimer’s disease.
According to a landmark paper published in Science Translational Medicine, the glymphatic system is 10 times more active during sleep than wakefulness. Think of it as a nightly cleaning service for your brain.
Without enough deep sleep, harmful waste can build up, contributing to cognitive decline, memory problems, and higher risks of neurodegenerative disease. In other words, skipping sleep is like skipping garbage day—the trash piles up until something breaks.
4. Emotional Regulation
Have you ever gone to bed upset and woken up calmer? That’s no accident. During REM sleep, the brain replays emotional events from the day but strips them of their most intense feelings. This is sometimes referred to as overnight therapy.
Dr. Matthew Walker, a neuroscientist at UC Berkeley and author of Why We Sleep, explains: “Sleep is the single most effective thing we can do to reset our brain and body health each day.” He notes that REM sleep acts like an emotional reset button, calming the brain’s amygdala—the region responsible for fear and aggression.
Neuroscientists have found that people deprived of REM sleep are 60% more reactive to negative stimuli than those who get a full night’s rest. That means sleep literally helps us manage feelings and face the next day with balance.
5. Immune System Boosting
While you sleep, your body produces cytokines, proteins that help fight infection, inflammation, and stress. These molecules are secreted only in meaningful amounts during sleep.
Research in Sleep journal found that people who slept fewer than six hours a night were four times more likely to catch a cold than those who slept seven hours or more. Another study showed that sleep-deprived individuals produced 50% fewer antibodies after a flu vaccine compared to well-rested participants.
In other words, sleep is a natural vaccine that trains your immune system every night. Missing it weakens your body’s first line of defense against illness.
6. Dreaming and Creativity
Dreams may feel random, but neuroscientists suggest they are the brain’s way of making connections and solving problems. In REM sleep, the brain weaves together information in novel ways, boosting creativity and insight.
Famous examples highlight this link between sleep and innovation:
Paul McCartney reportedly dreamed the melody for “Yesterday.”
Mary Shelley conceived the idea for Frankenstein after a vivid dream.
Dmitri Mendeleev claimed the periodic table came to him in his sleep.
Scientific evidence supports this: a Harvard Medical School study found that people who napped and entered REM sleep were 33% more likely to solve complex problems compared to those who stayed awake. Dreams are not just entertainment—they are cognitive laboratories.

Photo Credit: Pinterest
7. Hormonal Balancing
Sleep regulates some of the body’s most important hormones. During deep sleep, the brain adjusts the levels of:
Insulin (blood sugar control)
Leptin (satiety hormone)
Ghrelin (hunger hormone)
Cortisol (stress hormone)
When sleep is cut short, these hormones go haywire. Ghrelin rises, making you hungrier, while leptin drops, making you feel less satisfied after eating. Cortisol spikes, putting stress on your cardiovascular system. Insulin resistance increases, raising your risk of diabetes.
This explains why chronic sleep deprivation is linked to obesity, Type 2 diabetes, and heart disease.A report from the World Health Organization warns that populations with widespread sleep deprivation are at significantly higher risk for metabolic disorders.
8. Muscle Paralysis (Sleep Paralysis During REM)
Perhaps the most mysterious process of all: while dreaming in REM sleep, your body deliberately paralyzes itself. This phenomenon, called REM atonia, prevents you from physically acting out your dreams. Without it, people could thrash, run, or hurt themselves in bed.
In rare cases, people wake up before the paralysis has fully worn off—leading to the frightening experience of sleep paralysis. During such episodes, individuals are awake but unable to move, often experiencing vivid hallucinations. Though harmless, it offers a strange glimpse into how powerfully the brain controls the body during sleep.
Sleep disorders like REM Behavior Disorder (RBD) occur when this paralysis mechanism fails, causing people to physically act out their dreams, sometimes violently. This condition is not only dangerous but also considered an early warning sign of neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson’s.
Photo Credit: Pinterest
Why This Matters
Sleep is not wasted time, it is essential biological work. From memory to immunity, from emotional health to physical repair, these night time processes keep us functioning, learning, and thriving. Missing out on sleep means skipping body maintenance, brain cleaning, and emotional reset.
The takeaway is simple: the hours you spend asleep may be the most important investment in your physical and mental health. So the next time you think of cutting sleep short, remember—it’s the only time when your body and brain can do the critical things that literally keep you alive.
More Articles from this Publisher
World’s Strongest Currencies Compared to the U.S. Dollar

The Dollar may be powerful, but it’s far from the strongest. See the top currencies in the world that outshine it, and w...
World’s Strongest Currencies Compared to the U.S. Dollar

The Dollar may be powerful, but it’s far from the strongest. See the top currencies in the world that outshine it, and w...
Why Do Africans Become More African After Leaving Africa?

Why do Africans abroad suddenly embrace their roots with pride? From Afrobeats in London to Yoruba weddings in New York,...
The Hidden History of Beer: When Brewing Belonged to Women

Did you know women invented beer thousands of years ago while men took the credit? Discover the fascinating story of fem...
Cyclone Idai 2019: Southern Africa’s Deadliest Storm in a Generation
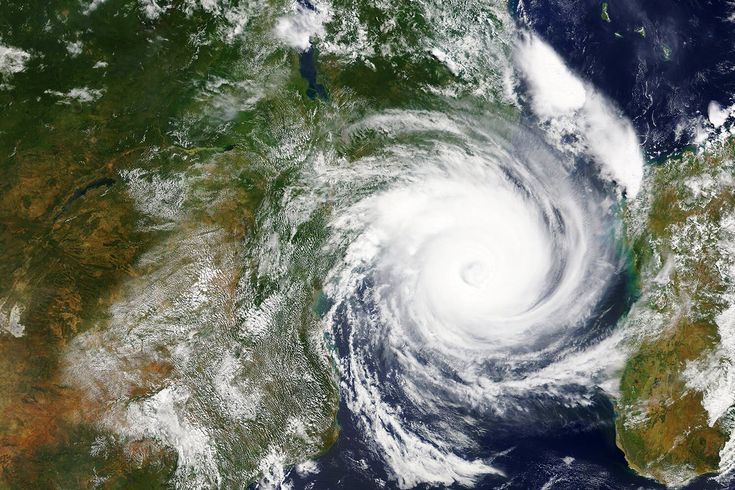

In March 2019, Cyclone Idai tore through Mozambique, Malawi, and Zimbabwe, killing over 1,500 people and displacing mill...
8 Things That Only Happen in Your Sleep And Why They Matter

Your brain cleans itself, your body heals, and your memories lock in. Here are 8 amazing things that only happen while y...
You may also like...
World’s Strongest Currencies Compared to the U.S. Dollar

The Dollar may be powerful, but it’s far from the strongest. See the top currencies in the world that outshine it, and w...
World’s Strongest Currencies Compared to the U.S. Dollar

The Dollar may be powerful, but it’s far from the strongest. See the top currencies in the world that outshine it, and w...
Why Do Africans Become More African After Leaving Africa?

Why do Africans abroad suddenly embrace their roots with pride? From Afrobeats in London to Yoruba weddings in New York,...
Boxing Icon's Son in Legal Turmoil: Julio Cesar Chavez Jr. Faces Cartel Allegations & Deportation Drama!

Mexican boxer Julio César Chávez Jr. has been deported from the U.S. to Mexico, where he was immediately jailed for alle...
Super Falcons Make History: Nigeria Crowned WAFCON Champions for 10th Time in Thrilling Win!
)
Nigeria's Super Falcons made history by clinching their 10th Women's Africa Cup of Nations title with a spectacular 3-2 ...
Paolo Sorrentino's 'La Grazia' Dazzles Venice, Earns Raves

Paolo Sorrentino's latest film, 'La Grazia,' captivated the Venice Film Festival, earning a four-minute standing ovation...
KPop Demon Hunters Ignites Oscar Buzz, Captivates Audiences

The animated film "KPop Demon Hunters" has emerged as a record-breaking global phenomenon, topping Netflix viewership ch...
Naira Marley Breaks Silence: Explosive Defense in Mohbad Case Rocks Nigeria!

Naira Marley has released a documentary sharing his side of the story regarding the tragic death of his former signee, M...