The 6G Race: Africa's Make-or-Break Moment in the Next Tech Revolution

The race for Sixth Generation, or 6G, mobile is a dream no more; it is real and is happening right now. At the same time that the West and Asia sprint toward defining what 6G will look like, Africa stands out at a crossroads. Not just as a consumer of tomorrow's connectivity but as a continent with the chance to decide whether it will leap ahead or be left watching from the sidelines.
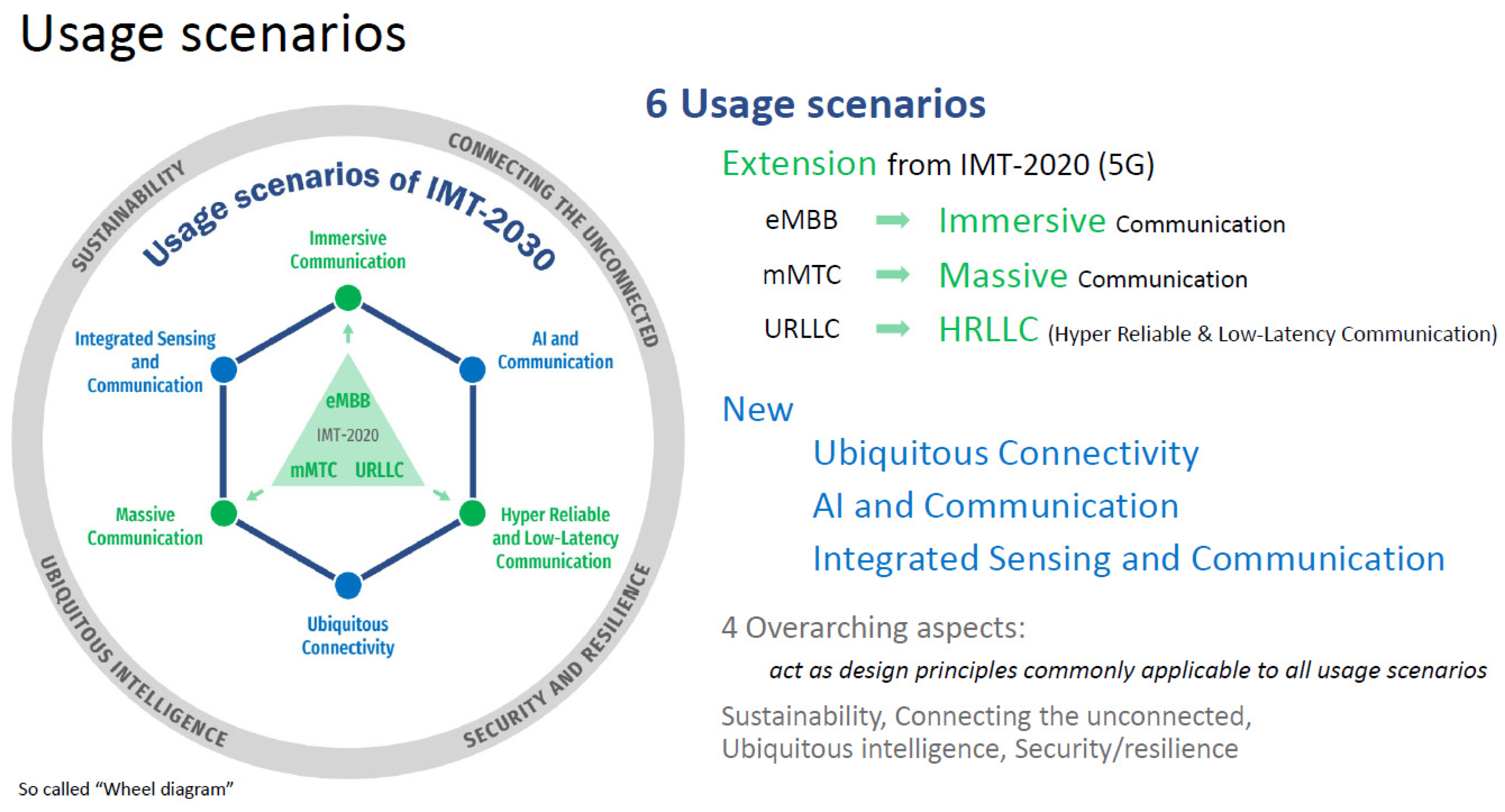
Expected to roll out around 2030, 6G promises more than simply faster downloads: speeds of 1 Tbps, near-zero latency, and networks able to sense, think, and communicate all at the same time through Integrated Sensing and Communication. This is the kind of technology that shapes economies, rewrites industries, and redefines power. And Africa, home to one of the youngest and fastest-growing populations on earth can’t afford to miss the moment.
A Leap Waiting to Happen
Africa has a history of skipping steps. The continent leapfrogged fixed telephone lines straight to mobile phones. It turned mobile money through systems like M-Pesa into a global case study. Now, 6G offers a similar window, only on a scale far greater than any before it.
This is what that leap could look like:
Precision Health and Education: Picture a world where a neurosurgeon in Johannesburg guides a complex operation in rural Uganda in real time with no lag or delay. Or where a teacher in Nairobi conducts a holographic classroom reaching students from Lagos to Lusaka. That is the promise of 6G's ultra-low latency (<0.1 milliseconds) combined with Tactile Internet; technology with responses faster than the human nervous system.
Climate and Food Security: With ISAC, 6G networks become intelligent sensor grids that can monitor soil health, detect pest infestations, and manage irrigation in real time. For a continent where agriculture employs over 60% of the population, this is innovation and it is survival.
New AI Ecosystem: Unlike 5G, 6G will be AI-native. Networks will be self-managing and capable of processing intelligence at the “edge”; closer to users rather than centralized data centers. That opens the door to African-built AI systems in everything from logistics to fintech to smart cities, tailored to local realities rather than imported from abroad.

The Harsh Reality: Infrastructure Can Break the Dream
The promise is dazzling-but the groundwork is fragile.
The Fiber Gap: The superfast THz signals of 6G cannot travel very far and would demand a web of small cells interconnected through huge fiber backbones. Yet, in 2025, most African countries are still struggling to finish national 4G rollouts; rural fiber remains spotty, and backhaul infrastructure is years behind what's required for 6G. Without it, even the best 6G innovation plans remain theory.
Cost vs. Commercial Reality: Not only will rolling out 6G be technologically challenging, but it is highly costly. The low ARPU in many African markets makes it hard to justify investment of billions into a network that only megacities might afford. Without creative financing or public–private partnerships, 6G could become another urban privilege rather than a continental equalizer.
The Digital Skills Gap: 6G won’t just need engineers—it’ll need quantum specialists, AI model trainers, and RF system architects. Right now, those skill sets are scarce on the continent. Without massive investment in STEM education and advanced digital literacy, Africa risks becoming a consumer of 6G, not a co-creator.
Africa's Moves on the Global Chessboard.
To its credit, Africa isn't waiting quietly on the sidelines. A coordinated push is already underway to make sure the continent isn't left out of the 6G conversation.
African Telecommunications Union (ATU): The ATU represents 52 member states and has become Africa's collective voice at the ITU, a global body responsible for shaping the 6G blueprint, officially known as IMT-2030.
The mission of the ATU is to ensure that the priorities of Africa in terms of affordability, energy efficiency, and rural inclusion are written into the DNA of 6G.
Betting on Open Networks: African operators are testing a different tack: open radio access networks, a modular technology approach that frees carriers from the few big telecom vendors. If adopted widely, Open RAN could drastically cut costs, encourage local innovation, and help Africa deploy faster and cheaper than traditional networks allow.
National Policy Blueprints: Countries such as Nigeria have integrated their 6G-Readiness into their National Digital Economy Policy. It focuses on three key building blocks: solid infrastructure, digital literacy, and emerging technologies, to create a launchpad for the next generation of connectivity.
Other nations, such as Kenya and Rwanda, are emulating similar measures with testbeds for AI-driven networks and digital twin experiments.

Why Does This Race Matters
The 6G race isn't about internet speeds; it is about the question of digital sovereignty. This entails who defines the rules of tomorrow's connected world. If Africa seizes this window, it could own a piece of the world's next great infrastructure, one built on innovation and inclusion.
Latest Tech News
Decode Africa's Digital Transformation
From Startups to Fintech Hubs - We Cover It All.
But should this moment be missed, the consequences could well reverberate for many decades to come: a whole continent of consumers dependent on imported intelligence, paying to use what others create. Which path Africa will take depends on the next five years, 2025-2030. Because 6G won’t wait.
The question is: will Africa?
Recommended Articles
There are no posts under this category.You may also like...
When Sacred Calendars Align: What a Rare Religious Overlap Can Teach Us

As Lent, Ramadan, and the Lunar calendar converge in February 2026, this short piece explores religious tolerance, commu...
Arsenal Under Fire: Arteta Defiantly Rejects 'Bottlers' Label Amid Title Race Nerves!

Mikel Arteta vehemently denies accusations of Arsenal being "bottlers" following a stumble against Wolves, which handed ...
Sensational Transfer Buzz: Casemiro Linked with Messi or Ronaldo Reunion Post-Man Utd Exit!

The latest transfer window sees major shifts as Manchester United's Casemiro draws interest from Inter Miami and Al Nass...
WBD Deal Heats Up: Netflix Co-CEO Fights for Takeover Amid DOJ Approval Claims!

Netflix co-CEO Ted Sarandos is vigorously advocating for the company's $83 billion acquisition of Warner Bros. Discovery...
KPop Demon Hunters' Stars and Songwriters Celebrate Lunar New Year Success!

Brooks Brothers and Gold House celebrated Lunar New Year with a celebrity-filled dinner in Beverly Hills, featuring rema...
Life-Saving Breakthrough: New US-Backed HIV Injection to Reach Thousands in Zimbabwe

The United States is backing a new twice-yearly HIV prevention injection, lenacapavir (LEN), for 271,000 people in Zimba...
OpenAI's Moral Crossroads: Nearly Tipped Off Police About School Shooter Threat Months Ago
ChatGPT-maker OpenAI disclosed it had identified Jesse Van Rootselaar's account for violent activities last year, prior ...
MTN Nigeria's Market Soars: Stock Hits Record High Post $6.2B Deal

MTN Nigeria's shares surged to a record high following MTN Group's $6.2 billion acquisition of IHS Towers. This strategi...
