BMC Medical Education volume 25, Article number: 622 (2025) Cite this article
Caring ability is a necessary ability for nursing staff, which can be improved through acquired training. The cultivation of students’ caring ability is the key to determine the quality of nursing in the future. While there is an extensive body of literature on the caring abilities of nursing students, numerous factors influence these abilities, and there remains a paucity of research on the nexus between self-compassion and caring ability. This study aimed to investigate the mediating roles of altruistic behavior and communication skills in the relationship between self-compassion and caring ability among nursing students.
The subjects of this study were 1567 undergraduate nursing students from four universities in different regions of China. An online survey was conducted using the Caring Ability Inventory (CAI), Self-Compassion Scale (SCS), Altruistic Behavior Questionnaire of College Students (ABQ-CS), and Supportive Communication Scale (SCS). SPSS 25.0 was utilized for descriptive analysis, independent sample t-tests, variance analysis, and Pearson correlation analysis. AMOS 23.0 was employed for mediation analysis.
The total scores of caring ability was 184.65 ± 23.65. The results showed that caring ability was significantly correlated with self-compassion(r = 0.614,P<0.001), altruistic behavior (r = 0.698,P<0.001) and supportive communication skills (r = 0.581,P<0.001). The direct effects of self-compassion (β = 0.304;0.259 ~ 0.349), altruistic behavior (β = 0.429;0.380 ~ 0.477), communication skills (β = 0.151; 0.110 ~ 0.194) on caring ability were confirmed. The self-compassion has indirect effects (β = 0.312;0.278 ~ 0.348) on caring ability by altruistic behavior and supportive communication skills among nursing student. The indirect effects accounted for total effect 30.88% with the direct effects accounted 69.12%.
The caring ability of nursing students is at the medium level. The altruistic behavior and communication skills of nursing students have mediating roles between self-compassion and caring ability. To improve caring ability for nursing students, educational strategies must be created to improve the self-compassion, altruistic behavior and communication skills. Interventions that self-compassion nursing students have the potential to enhance caring ability.
Care is at the core of nursing [1]. Watson defines caring as the moral concept of nursing that preserves human dignity, humanity, and integrity in the process of healing patients [1]. The ten caring factors proposed by Watson have clear guidelines for the cultivation of caring ability. The caring ability of nursing students in China is at a medium level [2–3]. It is crucial to cultivate caring abilities in nursing students.
Care is not decision by genes, it is transmitted by the culture of a society [1, 4]. Wang et al. reported that there are many factors affecting students’ caring ability, and the action path is complex [5,6,7]. Interventions targeted only at students’ caring ability have limited effects. Clarifying the action path of factors affecting students’ caring ability and taking measures to improve important influencing factors have important guiding significance for enhancing students’ caring ability. Therefore, based on Watson’s caring theory, this study starts from students themselves and explores the action path that affects their caring ability. It provides a scientific reference basis for nursing educators to formulate intervention plans.
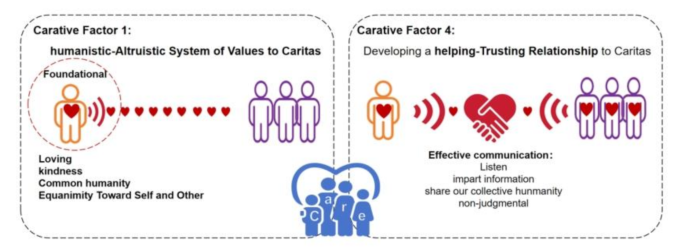
Just as shown in Fig. 1, Watson emphasized in Carative Factor 1 that self-care and compassion towards oneself are the prerequisites, foundation, and core factors for caring for others [1]. Self-compassion, proposed in the field of positive psychology, provides a new research direction for caring research. Self-compassion means that individuals do not avoid their own pain and failure, treat their own experience with tolerance, kindness and non-judgment, recognize that what they have encountered is part of the human experience, and reduce the pain experienced by individuals [8].
In the theory of caring, Watson emphasizes that nurses are always required to care for patients while ignoring their own care and compassion, which will lead to such undesirable phenomena as empathy fatigue and exhaustion [1]. In recent years, studies reported that self-compassion can improve the level of individual mental health and effectively reduce compassion fatigue and job burnout [7, 9,10,11]. Andrews’ grounded theory research found that nurses who care and empathize with themselves are better able to meet patients’ needs [12]. If a person is in emotions such as pain, sadness, and despair, they cannot feel sympathy and care for others [13]. Related research reports, self-compassion has a positive effect on the caring ability of nursing students [13–14].
Watson’s caring theory and these research findings indicate that it is only on the premise of nurses’ physical and mental health that positive emotional support and care can be provided for patients. Therefore, teaching students to correctly face difficulties and pressures and be kind to themselves can improve their humanistic care ability by enhancing students’ self-compassion [7]. This view has been confirmed in Zhang et al.‘s intervention study on self-compassion [7].
Watson proposed that cultivating nursing students’ altruistic values and altruistic behavior is the key to the formation of caring ability [1]. Altruistic behavior contributes to the healthy development of people’s body, mind and spirit, which is manifested as the dedication of willing to help others even if their own interests are damaged [15]. There is a significant positive correlation between altruistic behavior and caring ability of nursing students [16]. However, there are relatively few studies on the relationship between altruistic behavior, communication ability, and caring ability. Some studies have reported that individuals with high self-compassion are more inclined to support and help others, it is easier to show understanding and tolerance for the actions of others [17,18,19]. Research on self-compassion and altruism has found a significant positive correlation between self-compassion and altruism [15]. Intervention studies have reported that altruistic behavior can be promoted by improving the level of self-compassion [19]. Some researchers have found that altruistic behavior can’t only improve caring ability, but also promote the improvement of communication skills [16, 20].
According to Watson’s caring theory, communication skills are the way to realize caring [1]. As shown in Fig. 1, Watson put forward in Carative Factor 4 that effective communication possesses key elements such as listening, non-criticism and sharing common humanity. Effective communication is conducive to establishing trust relationships. Several studies have shown that there is a significant positive relationship between communication skills and caring ability of nursing students [4, 21,22,23]. Nursing students with strong communication skills are more likely to establish trust with others, form good interpersonal relationships, and promote the improvement of caring ability [4]. Individuals with high levels of self-compassion will reduce feelings of isolation, promote their communication skills, and help individuals establish positive relationships [9]. Phoebe’s research shows that increased self-compassion can promote communication behaviors [24]. Zhang and Fang believe that there is also a close relationship between altruistic behavior and communication ability [16, 20]. Based on these previous studies, it is analyzed that communication ability may be an important variable between self-compassion, altruistic behavior, and caring ability.
Therefore, in order to explore a new perspective for cultivating students’ caring ability, based on Watson’s caring theory and previous research results, the hypothesis is as follows:
H 1: Self-compassion has a direct effect on caring ability.
H 2a-c: Altruistic behavior has a direct effect on caring ability.
There was a correlation between altruistic behavior and communication skills.
Altruistic behavior has a mediating effect between self-compassion and caring ability.
H 3a-b: Communication skills has a direct effect on caring ability.
Communication skills is the mediating variable between self-compassion and caring ability.
This is a cross-sectional study using convenience sampling between June to November 2021 from four universities of China. Approval for this study was obtained from the ethics committee of the 2nd Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University (KY-2022-021). In this study, informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to the investigation, and guarantees were made to protect the anonymity and privacy of the participants’ information.
Participants and procedure
The eligible participants are full-time undergraduate students aged 16 and above. If students are diagnosed with any mental disorders (including depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, etc.), or if they are on leave of absence from school, demoted to a lower grade, transferred to another major, etc., they will be excluded. According to the requirements of structural equation model analysis, at least 300 samples are needed for the analysis.
Before the survey, the researchers trained the investigators through WeChat (a Social Media Applications). The investigators explained the purpose, content and significance of the research to the students, and the students answered voluntarily. The QR code of an online survey tool was distributed in nursing student’ chat group via WeChat by nursing teacher. A total of 1647 questionnaires were collected, and 1567 valid questionnaires were collected, with an effective recovery rate of 95.14%.
The Demographic Questionnaire was developed by the researchers in line with previous literature research and the objectives of this study [25–26]. The survey items include gender, Years of Education, Family with only child and Religion.
The Caring Ability Inventory (CAI), developed by Nkongho and translated into Chinese by Xu [25], is comprised of three subscales: knowing (14 items), patience (10 items), and courage (13 items). All items carry a seven-point range of responses, with 1 = strongly disagree and 7 = strongly agree. The total scores ranges from 37 to 259, with higher sores indicating better caring ability. The Chinese version of the scale selected for this study has good reliability and validity. The Cronbach’s α coefficient of this scale was 0.84 and content validity index was 0.78 in Xu et al. study [25].
The Self-Compassion Scale (SCS), was developed by Neff and translated into Chinese by Chen [26]. The scale consists of 26 items and six dimensions, including self-kindness (5 items), common humanity (4 items), mindfulness (4 items), self-judgment (5 items), isolation (4 items), and over-identified (4 items). These items are scored on a five-point Likert scale ranging from 1 (almost never) to 5 (almost always). The total scores ranges from 26 to 130, with higher scores indicating greater self-compassion lever. The Cronbach’s α coefficient and test-retest reliability of the scale are 0.84 and 0.89, respectively.
The Altruistic Behavior Questionnaire of College Students (ABQ-CS), a 7-point Likert scale consisting of 22 items developed by Li [27]. The scale comprises five dimensions: altruistic behavior responsibility (6 items), respect and care for others (3 items), care and concern for oneself (5 items), altruistic behavior performance (4 items), and self-interested behavior and concepts (4 items). Responses are made based on a range, from 1 = strongly disagree to 7 = strongly agree, with higher scores indicate that individuals have more altruistic behaviors. The Cronbach’s α coefficient of this scale was 0.873.
The Supportive Communication Scale (SCS) was developed by Whetten and translated into Chinese by Yuan [28]. The scale has 20 items and consists of 3 components: coaching and counseling (3 items), the supply of effective negative feedback (6 items), and supportive communication (11 items). It is a 5-point Likert scale with options ranging from 1 (I disagree a lot) to 5 (I agree a lot). The total scores ranges from 20 to 100, with higher scores indicating better communication lever. Cronbach’s alpha was 0.867.
Data analysis was performed using IBM SPSS version 25.0. First, descriptive statistics were used to describe the characteristics of the subjects. Second, a t-test and Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) were conducted to explore the statistical difference between characteristics and caring ability. Third, Pearson correlation analysis was used to explore the relationship between self-compassion, caring ability, altruistic behavior and communication skills.
AMOS 23.0 was used to mediation analysis. Examine the mediating effects of altruistic behavior and communication skills between self-compassion and caring ability.
Among the 1567 nursing students, there were 1340 (85.51%) female,227 (14.49%) male. The caring ability of female students was higher than that of male students(P<0.001). There was no significant difference in caring ability among different grades and religious beliefs(P>0.05). Table 1 presents their full demographics and group difference results for caring ability.
The average score on caring ability was 184.65, with a standard deviation of 23.65. The scores of knowing dimension, courage dimension and patience dimension were 76.55 ± 13.32, 49.31 ± 14.90 and 58.80 ± 9.19 (Table 2).
As presented in Table 3. The results showed that caring ability was significantly correlated with self-compassion(r = 0.614,P<0.001), altruistic behavior (r = 0.698,P<0.001) and communication skills (r = 0.581,P<0.001).
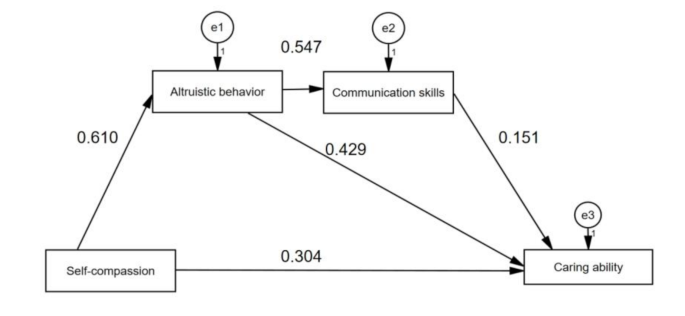
The evaluation index requirements for the overall model fit of the structural equation model are as follows: X2/DF between 1 and 3 indicates that the model has fitness, and GFI, AGFI, IFI, CFI, TLI > 0.9, SRMR, RMSEA < 0.05 indicate that the model fits well. As shown in Table 4, the model achieves a good fit to the data. The model and the effects estimate are showed in Table 5; Fig. 2.
As shown in Table 6, the direct effects of self-compassion (β = 0.304;0.259 ~ 0.349), altruistic behavior (β = 0.429;0.380 ~ 0.477),communication skills (β = 0.151; 0.110 ~ 0.194) on caring ability were confirmed. The self-compassion has indirect effects (β = 0.312;0.278 ~ 0.348) on caring ability by altruistic behavior and communication skills among nursing student. The total indirect effects accounted for 30.88% with the total direct effects accounted 69.12%.
The mediating effects of altruistic behavior and communication skills between self-compassion and caring ability in nursing undergraduates
This study examined caring ability among nursing students and the relationship between self-compassion, altruistic behavior and communication skills. In this study, the caring ability score of nursing students was 184.65 ± 23.65, which was roughly equivalent to that reported by Chen [26]. Caring ability of nursing students in the medium level. The results of the three dimensions of caring ability of nursing students showed that the score of courage was the lowest. This result is the same as that of Chen et al. ‘s survey of nursing students [26, 29]. The findings of Lv et al. on nurses showed that courage scored the lowest [30–31]. In the long process of learning, nursing students will constantly face failures and setbacks. Courage can make nursing students not afraid of failure and difficulties, which is one of the essential qualities [32]. Some studies have found that nursing students with extroversion are more courageous. Family, school and social environment can also influence courage [6, 32–33]. Therefore, future research can study the differences in the caring ability of nursing students with different personality traits.
The results of correlation analysis show that there is a significant positive correlation between self-compassion and caring ability (r = 0.614,P<0.001). The results of mediation analysis showed that there was a direct effect between self-compassion and caring ability (β = 0.304), accounting for 23.77% of the total effect value (H 1a was supported). Self-compassion can help individuals maintain a healthy mindset and positive emotions, enabling them to treat themselves and others kindly and tolerantly, which is a prerequisite for caring for others [1, 8, 34–35]. Nursing students with stronger self-compassion can treat themselves more kindly, view their own failures and setbacks objectively, overcome the fear brought by failures, and thereby enhance their courage in the face of difficulties [8]. When they are too harsh on themselves, they are more likely to have emotions such as sadness, distress, and despair, which may lead to ignoring the feelings and emotions of others, thus affecting their ability to take care of others. Students with a high degree of self-compassion are more tolerant of themselves and others, which makes them better able to understand, sympathize with, and care about others.
Students have relatively limited social experience and emotional encounters. When confronted with complex, negative and arduous setbacks, if schools, families and society can offer positive and constructive guidance, it is likely to significantly enhance students’ self-compassion levels and mental health. Consequently, this can improve their capabilities and behaviors in caring for others. Hofmeyer and his colleagues employed methods such as online courses to boost students’ self-compassion levels, and this approach has provided us with some inspiration [36].
This study found that altruistic behavior and caring ability (β = 0.429) has a direct effect, accounting for 33.54% of the total effect value (H 2a was supported). Communication skills and caring ability (β = 0.151) has a direct effect, accounting for 11.80% of the total effect value (H 3a was supported). Altruistic behavior and communication skills were the mediating variables between self-compassion and caring ability, and the indirect effect accounted for 30.88% of the total effect (H 2c and H 3b were supported).
There are two indirect effect paths between self-compassion and caring ability. Self-compassion has an indirect effect on caring ability through altruistic behavior. Watson proposed that altruistic values are one of the important components of caring ability [1]. Students with high self-compassion will change from paying attention to and caring about themselves to caring about and paying attention to the surrounding environment and people. While reducing their own negative emotions, they will have a positive and forward influence, making it easier for students to pass on kindness to others. Individuals with a high level of self-compassion will spread their kindness and kindness to others, resulting in altruistic behavior [4]. Hagerman believes that the positive impact of self-compassion on students’ physical and mental health helps to establish good interpersonal relationships [9]. Mirza and others share the same view. They believe that the level of self-compassion among students is very helpful for the practice of students’ altruistic behavior and helps them transition to the role of caring nurses [37]. Students help patients through practice with the theoretical knowledge they have learned, achieve the realization of self-worth, obtain a sense of happiness and satisfaction, generate altruistic motives, and promote the improvement of students’ caring ability. In the future, nursing educators should encourage nursing students to participate more in activities such as social volunteer services to promote the emergence of altruistic behaviors among them.
Another indirect path is that self-compassion affects caring ability through altruistic behavior and communication ability. Watson believes that when a person sees his own predicament in others or the predicament of others in himself, he will recognize that these are universal, thereby strengthening the connection with others and acknowledging the common humanity [1]. Related research shows that individuals with a high degree of self-compassion can recognize universal humanity, enhance connections with others, reduce loneliness, and promote communication skills [9, 14]. Care can only be realized in the process of interpersonal connection, Communication skills is an important way of interpersonal interaction [1]. This study shows that there is a significant positive correlation between altruistic behavior and communication skills (H 2b was supported). Altruistic behavior has a positive and facilitating effect on communication skills. Research reports that communication ability is one of the factors influencing caring ability [21, 23]. Individuals who are tolerant and friendly towards themselves are more likely to exhibit altruistic behaviors towards others. The emergence of altruistic behaviors can effectively promote the improvement of communication skills. Effective communication can eliminate misunderstandings, increase trust between people, enhance interpersonal relationships, and is of great significance for improving caring ability. This research result suggests to educators and managers that improving the communication skills of nursing students is an indispensable link for cultivating caring ability.
In this study, altruistic behavior and communication ability were used as important mediating variables to explain the path of action between self-compassion and caring ability. The results showed that self-compassion and altruistic behavior are variables that have a greater impact on caring ability. As a necessary implementation approach, communication skills are of great significance for cultivating students’ caring ability. At present, nursing educators attach great importance to the cultivation and evaluation of students’ caring ability in theoretical and practical teaching. Based on the results of this study, in the future, in students’ practical operation classes, various teaching methods such as multimedia, simulated patients, and situational teaching should be fully utilized to incorporate the cultivation of students’ communication ability. The evaluation of students’ communication ability should be promptly fed back to them to guide them to take the initiative and be positive in enhancing communication and establishing close connections with others and society. This is of great significance for improving students’ caring ability. The improvement of self-compassion can have very beneficial impacts on students’ altruistic behavior, communication ability, and caring ability. It is suggested that in the future, the formulation of education programs should start from the perspective of improving self-compassion of nursing students, cultivate their altruistic behavior and communication skills, so as to promote the improvement of nursing students’ caring ability.
There are several limitations to this study. Although the participants in this study were from 4 universities in different provinces of China and were not representative of nursing students. This study uses the self-report evaluation method, which may lead to biases. In the future, it is advisable to attempt a mixed research method that combines self-evaluation with other-evaluation, as well as qualitative and quantitative approaches, to conduct more in-depth research and exploration on this topic. This study is a cross-sectional investigation, and a longitudinal follow-up investigation should be carried out for nursing students in the future.
The study found that the caring ability of nursing students in China is at a medium level, educators should still pay attention to cultivating the caring ability of nursing students. To pay attention to the influence of self-compassion on caring ability of nursing students. Targeted interventions were adopted to improve self-compassion of nursing students, cultivate altruistic values of nursing students, promote their communication skills, and improve their humanistic care.
The datasets used and analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Sincerely thanks to all students who participated in the survey.
This study was funded by the 2019 Heilongjiang Provincial Higher Education Reform General Project.
Medical Ethics Committee of the Second Hospital of Harbin Medical University (KY-2022-021). All participants were informed and consented before conducting the research investigation. This study complied with the Declaration of Helsinki.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Not applicable.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/.
Su, H., Zhai, H., Li, Y. et al. The mediating effects of altruistic behavior and communication skills between self-compassion and caring ability in nursing undergraduates. BMC Med Educ 25, 622 (2025). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-025-07197-5