Cointelegraph Website Hacked by Phishing Attack
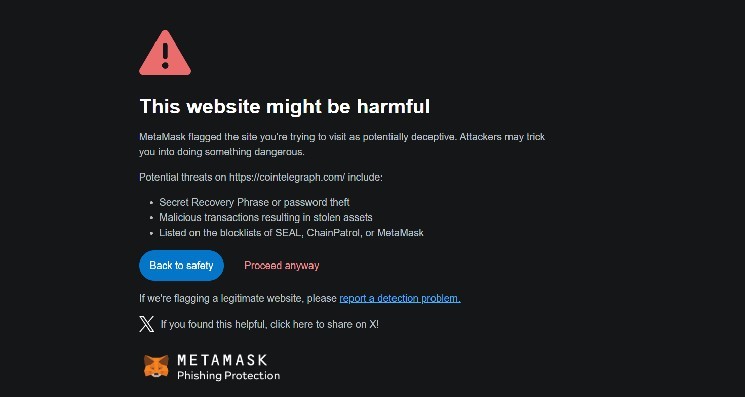
Crypto media outlet Cointelegraph confirmed its website was compromised by a front-end exploit on Sunday, with attackers injecting a malicious pop-up. This fraudulent banner falsely claimed to offer "CoinTelegraph ICO Airdrops" and "CTG tokens," enticing readers with a promise of nearly $5,500 worth of tokens. The scam leveraged a fabricated "fair launch" event and a bogus CertiK audit report to lend an air of legitimacy to its illicit intentions. Cointelegraph promptly issued a warning on X, advising users: "Do not click on these pop-ups, connect your wallets, or enter any personal information," while assuring the public that they were actively working on a fix.
Victims of such schemes are typically tricked into connecting their crypto wallets under various false pretenses, such as claiming token airdrops, verifying identity, or receiving loyalty rewards. Once connected, their funds are siphoned immediately by the attackers. This particular incident on Cointelegraph bears a striking resemblance to a nearly identical exploit that occurred on CoinMarketCap just two days prior. In both cases, attackers successfully embedded malicious code to serve wallet phishing prompts, effectively hijacking trusted platforms to bypass user skepticism and turn them into unwitting vectors for wallet drainers.
These incidents highlight a growing wave of sophisticated phishing attacks targeting crypto platforms through compromised user interfaces. In these scams, the allure of free tokens or the need for identity confirmation acts as a bait to trick users into connecting their digital wallets, only for their accounts to be subsequently drained. According to blockchain intelligence firm TRM Labs, phishing schemes and malware-based infrastructure attacks accounted for a significant 70% of the $2.2 billion stolen in crypto-related hacks in 2024. The Cointelegraph compromise also follows closely on the heels of security researchers disclosing a massive data dump containing over 16 billion stolen login credentials, which likely originated from infostealer malware, credential stuffing, and previous data breaches, further underscoring the pervasive nature of cybersecurity threats in the digital asset space.










