AR-VR Technologies & Cultural Heritage

India is increasingly recognizing the imperative to harness advanced technology, including Artificial Intelligence (AI) and digital tools, to safeguard and promote its invaluable cultural heritage for future generations. The integration of such innovations promises a transformative approach to preserving historical artifacts and sites, making them globally accessible, and enhancing scholarly research and public appreciation.
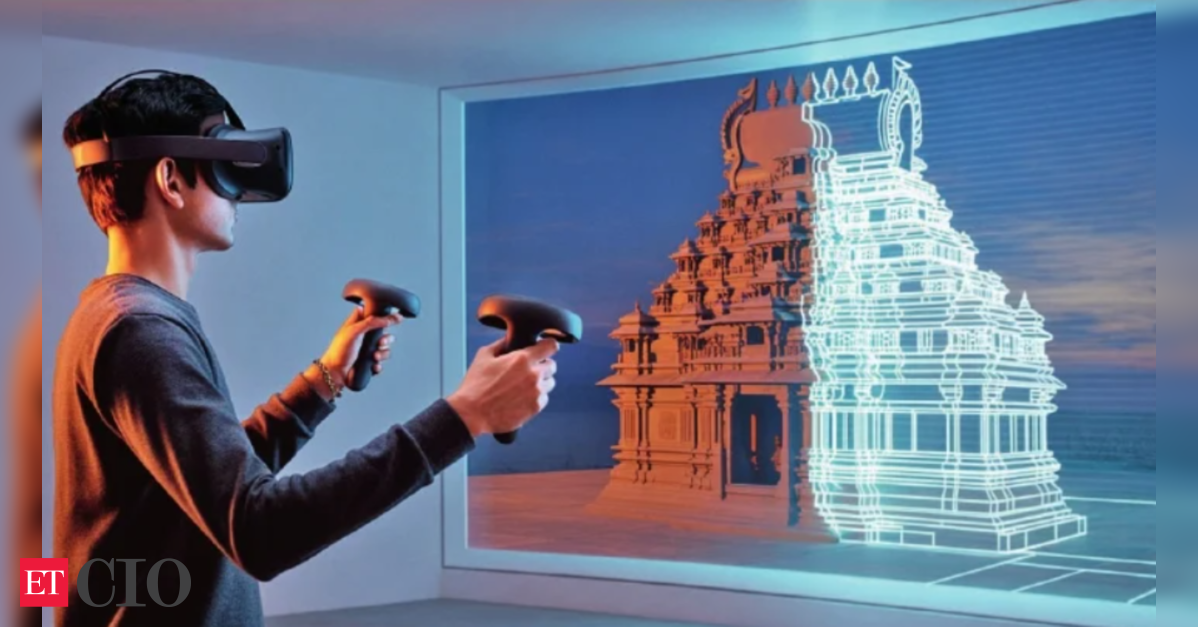
Digital technologies like high-resolution imaging and 3D modeling are crucial for creating resilient digital archives, protecting physical artifacts from degradation, and ensuring their longevity. AI further augments preservation efforts by analyzing environmental factors contributing to deterioration, predicting potential damage, and enabling precise restoration. Beyond preservation, Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) offer immersive experiences, democratizing access to historical sites and artifacts for those unable to visit in person. These tools can facilitate interactive virtual guides, personalized tours, and predictive maintenance for heritage locations.
Despite India’s vast array of historical landmarks and cultural treasures, leveraging these advanced technologies faces significant challenges. Current initiatives include virtual exhibits of the Ajanta caves and VR recreations of the Ellora caves, alongside private efforts showcasing Rajasthan forts. However, limited technological infrastructure, insufficient funding, skill shortages, and the persistent digital divide hinder widespread adoption. To overcome these barriers, strategic investments in infrastructure, increased government funding, partnerships with tech firms, and comprehensive training programs are essential.
A critical component of this technological shift involves adapting academic curricula, particularly for students of History and Museology. It is imperative to integrate technical proficiency, interdisciplinary collaboration, and practical training into their studies. This includes teaching digital tools such as Geographic Information Systems (GIS), virtual reality applications, and database management systems, which are vital for modern archival practices and the presentation of cultural heritage. Additionally, quantitative historical analysis and digital humanities can foster critical thinking and data literacy, while interdisciplinary electives and modules on grant writing and marketing prepare students for managerial challenges in the sector.
AI also holds transformative potential in pedagogical innovation, enhancing experiential learning and assessment. AI-driven simulations and virtual environments can provide practical, risk-free scenarios for students. In the context of learning, AI facilitates gamification and enables effective interdisciplinary teamwork through AI-powered collaborative platforms. For assessments, AI improves accuracy through automated grading systems, holistic performance analysis, and predictive analytics, guiding professors to adopt proactive teaching strategies. For universities to effectively incorporate AI, they must develop robust digital infrastructures, train faculty in AI applications, and establish ethical frameworks to ensure data security and algorithmic fairness.
Furthermore, technology plays a vital role in addressing contemporary challenges like historical misinformation and fake news. AI tools, such as advanced fact-checking systems and natural language processing, can cross-check historical claims against verified sources, detect misinformation patterns, and ensure accuracy. AR-VR technologies can provide immersive engagement with historical events, allowing students to experience key moments authentically, while digital libraries enhance accessibility to primary sources, promoting a deeper understanding of history. By embracing these technological advancements, India can ensure the longevity of its cultural legacy, connecting past and future generations with an authentic and accessible understanding of its rich heritage.